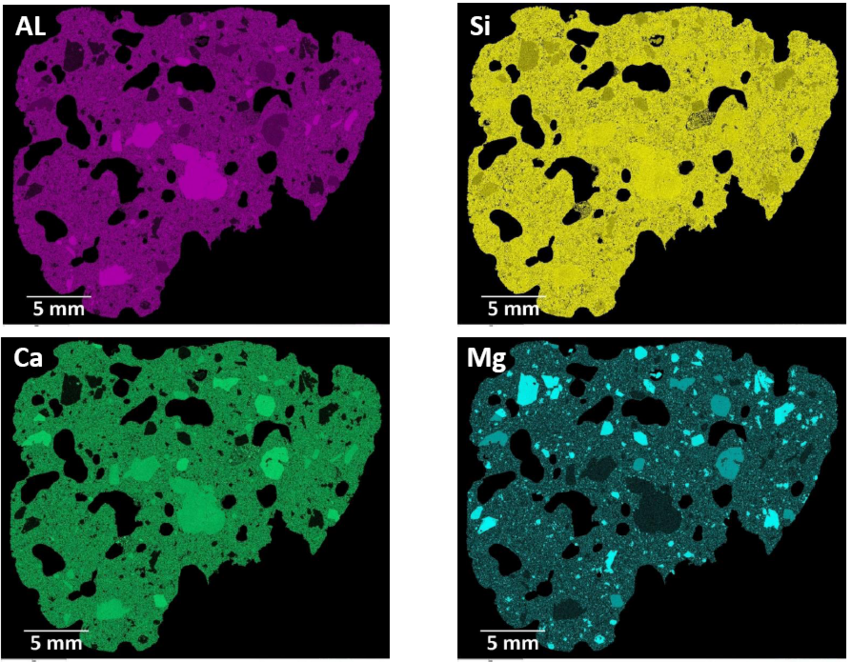
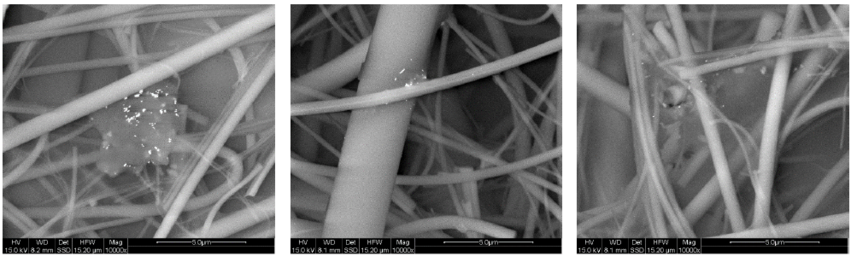
Dust is composed of particles of organic and inorganic substances of different size, origin and structure. The quantitative dust load is described on the basis of the mass of different size fractions, new analysis possibilities of dusts enable the allocation to emission sources on the basis of qualitative investigations.
Dust sources can be internal or external: Abrasion of building and equipment materials and electrical appliances, paintwork, combustion processes (open flames, cigarette smoke) or emissions from traffic and industry contribute to dust pollution in the interior. Dust can have negative effects on health and should therefore be regarded as risk factors indoors.
Very small particles in the air are transported with gases, absorbed during breathing and thus enter the human material cycle. This can lead to irritation of the respiratory tract and allergies, in the worst case to lung cancer. In particular, the length/diameter ratio of dust particles is relevant with regard to health effects: Asbestos and KMF dusts are carcinogenic, but hardwood fibres or highly alkaline dusts such as cement dust can also have serious health effects if exposed for an appropriate period of time.
Within the scope of the project different sampling methods for dust analysis are tested (air sampling, suction with special filters, surface samples), simulation calculations of dust transport by convection are carried out and particle analyses are carried out using a scanning electron microscope. In addition, the correlation between dust concentration, composition and physiological parameters is investigated.